
Employers now place high value on both technical and soft skills. Organizations increasingly seek professionals who combine hands-on expertise with strong interpersonal abilities. Technical knowledge alone is no longer enough for success.
For example, a recent industry study found that 84% of managers say new hires must demonstrate strong soft skills like communication and teamwork. At the same time, most young people recognize the importance of digital know-how: 88% of workers aged 16–24 believe technical or “digital” skills are critical for their future careers.
In other words, both sides of the skills coin are in high demand. As businesses adopt new technologies, they need employees who can use tools like data analytics or cloud computing effectively and collaborate, lead projects, and adapt to change.
These trends raise key questions: What is the difference between technical and soft skills? And how can professionals find the right balance between them? The following sections dig deeper into these questions. We’ll compare and contrast technical vs soft skills, explore examples from IT, engineering, business, and healthcare, and look at why both sets of skills will matter even more in the future.
Difference Between Technical Skills and Soft Skills
Technical skills vs soft skills form the foundation of a successful career, but they differ significantly in what they represent, how they’re learned, and how they contribute to professional growth. Understanding their differences helps individuals build a well-rounded skill set that aligns with changing job demands.
1. Nature of Skills
- Technical skills (also called hard skills) are teachable and measurable abilities. They are directly related to performing specific tasks or using certain technologies. Examples include programming, data analysis, cybersecurity, and operating machinery. These skills are often gained through formal education, certifications, or on-the-job training.
- Soft skills, on the other hand, refer to interpersonal and behavioral traits. They determine how a person communicates, leads, adapts, and collaborates with others. Skills like empathy, adaptability, and problem-solving fall under this category. They are usually learned through life experience, feedback, mentorship, and ongoing self-development.
2. Transferability
- Technical skills are usually domain-specific. For example, a data analyst’s proficiency in R or Python might not be directly useful in a customer service or marketing role without retraining.
- Soft skills are highly transferable. Working in a team, resolving conflicts, or communicating effectively is valuable across diverse roles and industries, whether in healthcare, education, or tech.
3. Learning & Measurement
- Learning technical skills involves structured approaches: taking courses, attending bootcamps, getting certifications, and engaging in hands-on practice. Progress is clearly defined—master one skill, then move to the next. Employers assess them through tests, coding tasks, or project-based assignments.
- Soft skills, in contrast, are learned informally and evaluated subjectively. They grow through work experience, mentorship, coaching, and handling real-life challenges. Peer reviews, behavioral interviews, and managerial feedback are common ways of measuring them, though assessments may vary widely by context.
4. Longevity and Relevance
- Technical skills can become outdated quickly due to technological advances. A programming language or software tool in demand today might lose relevance in a few years. Continuous learning is essential.
- Soft skills retain long-term relevance. The ability to lead a team, resolve conflicts, or think critically remains important regardless of industry changes or technology shifts. As industries transform, soft skills help employees adapt to new tools and environments.
Related reading: How to Increase the Productivity With IT Staff Augmentation
Technical Skills vs Soft Skills Examples
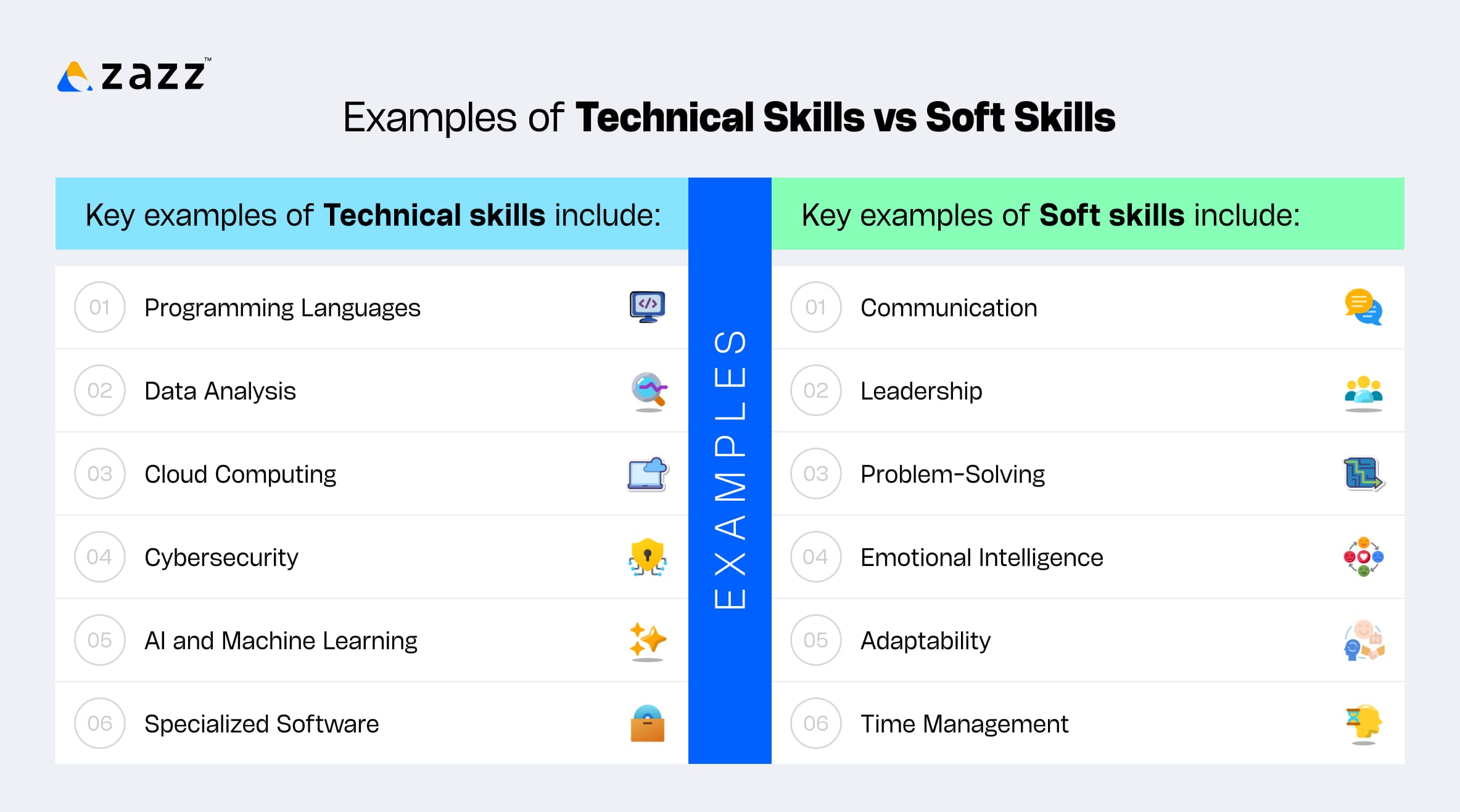
Key examples of technical skills include:
- Programming Languages: Proficiency in Python, Java, JavaScript, and C++ enables developers to create software products. The 2024 Stack Overflow Developer Survey found that JavaScript is used by 62% of developers, with Python at 51%.
- Data Analysis: Analysts use tools like SQL, R, and Excel to interpret datasets, drive decision-making, and build predictive models.
- Cloud Computing: Skills in deploying and managing cloud infrastructure on platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure are in high demand.
- Cybersecurity: Knowing how to set up firewalls, encrypt data, and perform ethical hacking protects organizational assets. Fortinet reports a significant cybersecurity skills gap, with 70% of IT leaders citing it as a risk.
- AI and Machine Learning: Building neural networks, understanding algorithms, and working with frameworks like TensorFlow are increasingly valuable in technical fields.
- Specialized Software: In sectors like design or manufacturing, proficiency in CAD software or operating CNC machines is often required.
Key examples of soft skills include:
- Communication: Clear writing, active listening, and explaining complex topics to diverse audiences improve collaboration and efficiency.
- Leadership: Inspiring teams, resolving conflicts, and managing goals are traits associated with strong leadership.
- Problem-Solving: Thinking critically under pressure, evaluating alternatives, and making effective decisions are highly valued in dynamic workplaces.
- Emotional Intelligence: Recognizing and managing emotions—both one’s own and others’—strengthens relationships and improves conflict resolution.
- Adaptability: Being open to change, learning new tools, and handling ambiguity allows professionals to stay relevant.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks, meeting deadlines, and staying organized contribute to productivity and reliability.
The Future of Work: A Shifting Landscape

The way we work is evolving faster than ever before, driven by advancements in technology, changing workforce expectations, and global shifts in how businesses operate. As we move forward, both technical skills vs soft skills will play an increasingly interconnected role in shaping future careers.
AI and Automation
As artificial intelligence (AI) and automation reshape industries, routine and repetitive tasks are increasingly being handled by machines. Tasks like data entry, scheduling, and even basic analytics are now automated with software and AI tools. However, this shift doesn’t render humans obsolete—it redefines their role.
Human workers are still essential for tasks that require emotional intelligence, ethical judgment, critical thinking, and creativity. For instance, while AI can analyze patterns in large datasets, it’s the human strategist who interprets those patterns in context and makes decisions aligned with business goals or social impact. Similarly, AI might assist in drafting reports or emails, but nuanced communication, especially in leadership, negotiations, or sensitive scenarios, still depends on human capabilities.
According to LinkedIn’s 2024 report, skills such as adaptability, creativity, and communication are rapidly rising in importance. These soft skills complement technical advancements and help organizations navigate the fast-evolving digital landscape.
Remote and Hybrid Work
The post-pandemic world has ushered in a new era of work flexibility. Remote and hybrid work models have become the norm for many organizations, making soft skills like virtual communication, self-motivation, and accountability more critical than ever.
Without the structure of a physical office, employees must manage their schedules, meet deadlines independently, and communicate clearly across digital channels like Zoom, Slack, or Teams. Trust becomes a cornerstone as team members are expected to deliver results without constant oversight.
On the technical side, remote work also demands digital fluency. Employees must be comfortable navigating collaboration tools, handling digital security, and using cloud-based systems. Understanding how to manage shared drives, maintain cybersecurity hygiene, and troubleshoot minor IT issues is now an essential technical skill for remote professionals.
A successful remote worker today blends self-discipline and interpersonal effectiveness with solid digital know-how.
Digital Transformation
Across industries, organizations are undergoing rapid digital transformation. From hospitals deploying AI for diagnostics, to banks developing user-friendly fintech apps, to schools shifting to virtual classrooms, technology is embedded in the core of service delivery.
These advancements demand a significant boost in technical skills. Employees need to upskill in areas such as cloud computing, cybersecurity, data analytics, and software implementation. However, technology alone isn’t enough.
The real success of digital transformation lies in change management, employee engagement, and inclusive leadership. People must be trained to use new tools effectively. Managers must foster a culture that embraces innovation, reduces resistance, and builds confidence in the new systems.
Soft skills such as leadership, training, empathy, and communication are key to ensuring that digital transformation doesn’t just occur but thrives.
Related reading: 5 Benefits of Nearshore Staff Augmentation
4 Real-World Examples: How Leading Companies Prioritize Skills

In today’s fast-evolving workplace, leading organizations recognize that success depends on both technical expertise and human-centric capabilities. Below are examples of companies that effectively invest in and balance these essential skill sets.
1. Google
-Soft Skills Drive Team Success
Through its internal Project Aristotle study, Google found that team performance was most influenced by psychological safety, empathy, and communication, not just technical brilliance. Today, Google balances technical excellence with training in collaboration, emotional intelligence, and inclusive leadership.
2. Salesforce
-Blending Digital Know-How with Emotional Intelligence
Salesforce trains its global workforce through Trailhead, a platform offering both technical modules (like cloud architecture) and soft skills (such as mindfulness, leadership, and inclusive communication). The result is a well-rounded, future-ready team that serves customers effectively.
3. Cleveland Clinic
-Empathy as a Core Skill in Healthcare
Known for medical innovation, the Cleveland Clinic also emphasizes soft skills like empathy and active listening. Staff undergo communication training to complement their technical expertise, leading to improved patient outcomes and higher satisfaction ratings.
4. Duolingo
-A Startup Balancing Engineering with User-Centered Design
The language-learning app relies on strong technical skills (machine learning, gamification) but also prioritizes collaboration between engineers, designers, and educators. This cross-functional teamwork helps Duolingo continuously improve its user experience.
Balancing Both Skills
In the modern workplace, when comparing technical skills vs soft skills, relying solely on either is no longer enough. The most successful professionals and organizations blend both to navigate complex challenges, drive innovation, and foster meaningful collaboration. Technical skills ensure tasks are completed efficiently and accurately, while soft skills like communication, adaptability, and empathy help teams work cohesively, adapt to change, and build strong relationships.
This balance is especially vital in cross-functional teams, where developers, marketers, and business leaders must communicate effectively to align goals and solve problems creatively. Moreover, companies that prioritize both skill sets are better positioned for long-term growth, as they cultivate agile talent capable of learning new technologies while also leading, mentoring, and collaborating. In short, technical know-how powers progress, but soft skills sustain it.
Conclusion: Building a Future-Proof Skill Set
As the workplace continues to evolve, professionals must recognize that career success depends on a strong mix of technical skills vs soft skills. Mastery of tools like data analytics, cloud platforms, or AI frameworks is essential, but so is the ability to lead teams, communicate across functions, and adapt to change.
Key Takeaways:
- Technical skills are crucial for executing tasks, staying updated with technology, and meeting job-specific requirements.
- Soft skills drive collaboration, leadership, emotional intelligence, and the ability to thrive in dynamic environments.
- The most in-demand professionals are those who can bridge both worlds—using technical expertise to solve problems and soft skills to influence outcomes.
Related reading: Tech Recruiting Guide: 10 Tips to Hire Tech Talent
Actionable Tips:
- Invest in Continuous Learning: Take online courses or certifications in emerging technologies relevant to your field.
- Practice Communication: Join team projects, lead meetings, or participate in public speaking forums to refine how you present ideas.
- Seek Feedback: Ask mentors or peers to evaluate both your technical output and interpersonal style.
- Work Cross-Functionally: Collaborate with departments outside your area to better understand how technical and soft skills intersect.
- Stay Curious and Agile: Embrace change, experiment with new tools, and reflect on experiences to build resilience.
In a future shaped by automation, digital transformation, and hybrid work, the professionals who thrive will be those who can code, collaborate, analyze, empathize, and lead. Now is the time to build that balanced skill set.
At Zazz, we turn skills into career success. Join us to grow, lead, and make an impact.
Frequently Asked Questions
Because technology is rapidly evolving, employers need professionals who can not only use tools effectively (technical skills) but also collaborate, communicate, and adapt in dynamic work environments (soft skills).
Technical: Data analysis, cloud computing, AI/ML, cybersecurity.
Soft: Communication, adaptability, leadership, problem-solving.
Practice active listening, seek feedback, take part in team projects, and consider mentorship or training in areas like emotional intelligence or public speaking.
Soft skills are often developed through real-world experience and reflection, making them less structured to learn but equally (if not more) essential over time.
Soft skills are interpersonal abilities like communication, teamwork, and adaptability. Technical skills are job-specific abilities like coding, data analysis, or using software tools.
Technical skills focus on using specific tools and technologies, while soft skills relate to communication, leadership, and collaboration.
Recent Articles
Table of Content 1. Difference Between Technical Skills and Soft...
Table of Content 1. How Automation is Positively Impacting Careers...
Table of Content 1. Skills and Workforce Evolution 2. Top...
















